CI pipelines are supposed to accelerate development—but when a single test fails, everything stops. Developers drop what they’re doing, open logs, scroll through stack traces, and manually track down the issue. It’s disruptive and pull attention away from more meaningful work.
AI-Driven CI is here to change that: coupling Semaphore with GitHub Copilot Agents makes creates the opportunity for self-healing pipelines.
In this guide, we’ll walk through exactly how to set up this integration and how you can use it to transform routine CI maintenance into a fully automated, self-healing process. For a step-by-step tutorial, check out our documentation page.
Self-healing Pipelines
Instead of treating failures as static events, Semaphore forwards them to GitHub Copilot Agents, which act as automated problem-solvers inside your development workflow. When a job fails, Copilot receives:
- the failure context,
- the test output,
- a prompt that requests to fix the CI
From there, Copilot begins working like a developer assigned to the task: it reads the issue, analyzes the test results, identifies the likely fix, and prepares a Pull Request with corrections.
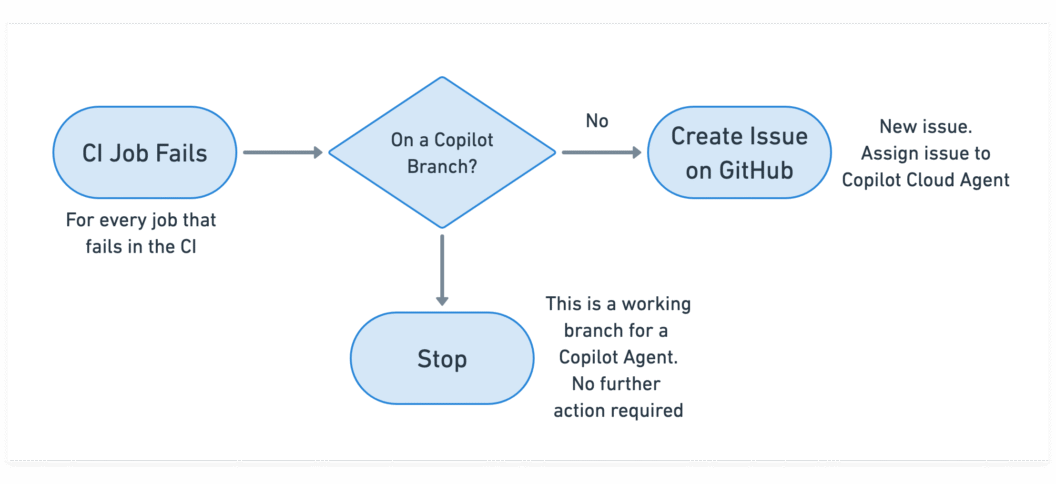
The result is a lightweight, cloud-driven self-healing mechanism that works alongside your existing CI without additional infrastructure, custom runners, or no workflow redesign required.
Prerequisites
Before connecting Semaphore with GitHub Copilot Agents, there are a few requirements to set up. These ensure that Semaphore can communicate with GitHub securely and that Copilot has permission to act on your repository.
GitHub Personal Access Token (PAT)
Semaphore needs permission to create issues and pull requests on your behalf.
To enable this, generate a GitHub Personal Access Token with the following scopes:
- repository: full read/write access
- read:org: so the CI can access your GitHub organization
This token will later be added as a secret in Semaphore so your pipelines can call the GitHub API.
Copilot Agents Enabled in Your GitHub Organization
The integration relies on GitHub Copilot’s Cloud Agents, which run fixes in an isolated hosted environment.
Your organization needs a plan that supports them:
- Copilot Pro
- Copilot Pro+
- Copilot Business
- Copilot Enterprise
You can confirm this under: GitHub → Organization Settings → Copilot → Agents
(Optional but Highly Recommended) Test Reports
Copilot Agents work best when they have structured test output to analyze. If your project doesn’t already produce JUnit XML reports, you can enable them in Semaphore’s test reporting feature
Setting Up the Integration
With the prerequisites in place, you can now connect Semaphore to GitHub Copilot Agents. The setup is lightweight and only needs a few adjustments to your CI configuration. Once done, every failing job in your pipeline can automatically generate a Copilot-driven fix.
Add GitHub Token Secret
Semaphore needs secure access to GitHub’s API to create issues and PRs. To enable this:
- Open your project in Semaphore.
- Navigate to Secrets → Create Secret.
- Name the secret:
gh-cli - Inside the secret, add the environment variable:
GH_TOKEN = <your GitHub Personal Access Token>
This secret will be attached to CI blocks later so they can call the GitHub CLI without exposing credentials.
Disable Workflow Runs for Draft Pull Requests
Copilot creates draft Pull Requests while it’s working and often updates them several times. You don’t want Semaphore running a full pipeline for each draft update.
To prevent unnecessary CI runs:
- Go to your project’s Settings.
- Find Build Pull Requests from Forks / Draft PRs.
- Set Draft Pull Requests → Disabled.
This ensures that only finished Copilot PRs trigger CI, not intermediate work.
Create a Prompt Template for Copilot
Copilot needs clear instructions on how to approach a failing job.
To provide this, add a text file in your repository:
prompt-template.txtA minimal example:
Read the following JUnit test report, diagnose the failure, and create a Pull Request with the fix.
Validate the fix before creating the Pull Request.You can expand the prompt with:
- coding standards
- architectural constraints
- preferred file locations
- specific test commands
Add Copilot Trigger Logic to Failing CI Blocks
Finally, update any block in your Semaphore pipeline that might fail due to tests or builds.
In each such block:
- Attach the GitHub Token Secret
- In the Epilogue section “If job has failed”, add the following commands:
cp prompt-template.txt prompt-issue.txt
echo '```xml' >> prompt-issue.txt
cat results.xml >> prompt-issue.txt
echo -e '\n```' >> prompt-issue.txt
[[ ! "$SEMAPHORE_GIT_WORKING_BRANCH" =~ ^copilot/ ]] && \
gh issue create \
--assignee "@copilot" \
--title "Fix failed job: ${SEMAPHORE_JOB_NAME}" \
-F prompt-issue.txtThis snippet:
- copies your prompt template
- appends the relevant test report (
results.xml) - avoids loops by ignoring branches created by Copilot
- opens a GitHub issue containing everything Copilot needs to begin working
- Repeat this for any block you want Copilot to auto-repair.
How to Follow the Agent Activity
Once your integration is in place, Copilot Agents begin working automatically whenever a pipeline failure occurs. GitHub provides several places to observe what the agent is doing, how far along it is, and whether a fix is ready for review.
Here are the three main places to monitor Copilot Agent activity:
- Copilot Tasks Dashboard
- GitHub Issues in your repository
- GitHub pull requests in your repository
As Copilot works, it continually updates the issue and pull request threads. This makes issues the most detailed, narrative view of the agent’s reasoning and actions.
Final words
GitHub Copilot’s automated reasoning combined with Semaphore’s logic and context unlocks a powerful new development workflow: a CI pipeline that repairs itself.
The setup requires only a few additions to your existing pipeline, but the payoff is substantial:
- Faster feedback loops
- Fewer interruptions for developers
- Consistently healthy builds
- Automated issue creation and PR generation
- A predictable, AI-driven path from failure to fix
As AI-driven tooling becomes more integrated into everyday software development, self-healing pipelines will become more and more common. In fact, if you prefer to use a different agentic AI, we’ve covered Codex and Claude Code on a past post, so be sure to check that out.
Happy building and welcome to the AI-powered era of CI.
Want to discuss this article? Join our Discord.
